



This is an encoding technique which has three voltage levels namely +, - and 0. Such a signal is called as duo-binary signal.
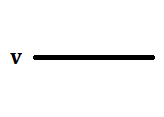
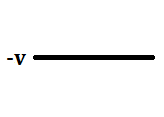
An example of this type is Alternate Mark Inversion(AMI). For a 1, the voltage level gets a transition from + to – or from – to +, having alternate 1s to be of equal polarity. A 0 will have a zero voltage level.
Select RZ/NRZ from below tabs-
In RZ Bipolar line coding, signal return to zero at the middle of the bit and follows the above described bipolar properties.
The functions for 0 and 1 bits are described below:
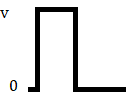

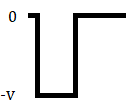

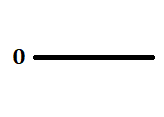
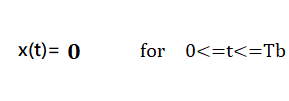
In NRZ Bipolar signal does not return to zero at the middle of the bit and follows the above described bipolar properties.
The functions for 0 and 1 bits are described below:
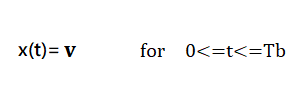
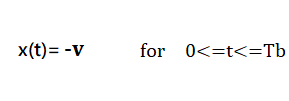

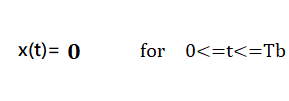

** Hover over RZ/NRZ graphs for more info
NRZ
Advantage: NRZ encoding requires less Bandwidth as it requires one transition only to encode one bit.
Disadvantage: As continuous set of zeros or ones is transmitted, self-synchronization is a problem in NRZ encoding.
RZ
Advantage: The transition at the middle of bit in Return-to-zero(RZ) provides better synchronization.
Disadvantage: To Encode one bit in Return-to-zero(RZ) encoding, two transitions are required. So, it is requires more Bandwidth.