



Select RZ/NRZ from below tabs-
In this type of Polar signaling, a High in data, though represented by a Mark pulse, its duration T0 is less than the symbol bit duration. Half of the bit duration remains high but it immediately returns to zero and shows the absence of pulse during the remaining half of the bit duration.
However, for a Low input, a negative pulse represents the data, and the zero level remains same for the other half of the bit duration. The following figure depicts this clearly.
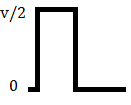

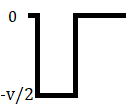

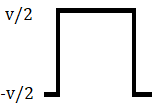
In this type of Polar signaling, a High in data is represented by a positive pulse, while a Low in data is represented by a negative pulse.
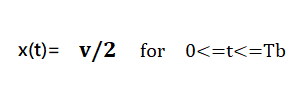
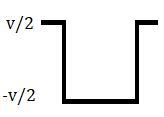
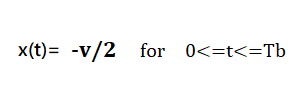

** Hover over RZ/NRZ graphs for more info
NRZ
Advantage: NRZ encoding requires less Bandwidth as it requires one transition only to encode one bit.
Disadvantage: As continuous set of zeros or ones is transmitted, self-synchronization is a problem in NRZ encoding.
RZ
Advantage: The transition at the middle of bit in Return-to-zero(RZ) provides better synchronization.
Disadvantage: To Encode one bit in Return-to-zero(RZ) encoding, two transitions are required. So, it is requires more Bandwidth.