Enter 5 numbers
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:

Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
Sorted Array:
No. of instructions count:
COUNTING-SORT(A, B, k)
k: upper range of input numbers
1. for i <- 0 to k
2. do C[i] <- 0
3. for j <- 1 to length[A]
4. do C[A[j]] <- C[A[j]] + 1
5. for i <- 1 to k
6. do C[i] <- C[i] + C[i - 1]
7. for j <- length[A] downto 1
8. do B[C[A[j]]] <- A[j]
9. C[A[j]] <- C[A[j]] - 1
#include <stdio.h>
int count=0;
void counting_sort(int A[], int k, int n)
{
int i, j;
int B[15], C[100];
count++;
for (i = 0; i <= k; i++)
{
C[i] = 0;
count++;
}
count++;
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++){
C[A[j]] = C[A[j]] + 1;
count++;
}
count++;
for (i = 1; i <= k; i++){
C[i] = C[i] + C[i-1];
count++;
}
count++;
for (j = n; j >= 1; j--)
{
count++;
B[C[A[j]]] = A[j];
count++;
C[A[j]] = C[A[j]] - 1;
count++;
}
printf("The Sorted array is : ");
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d ", B[i]);
}
/* End of counting_sort() */
/* The main() begins */
int main()
{
int n, k = 0, A[15], i;
printf("Enter the number of input : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("\nEnter the elements to be sorted :\n");
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &A[i]);
if (A[i] > k) {
k = A[i];
}
}
counting_sort(A, k, n);
printf("insrtructions count=%d",count);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
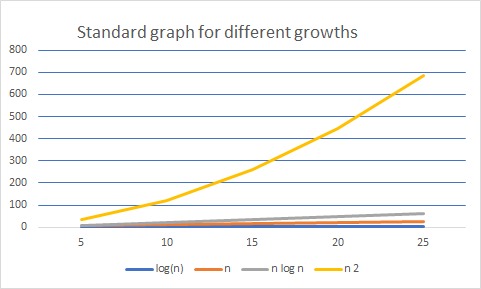
| Best case | |
| Average case | |
| Worst case |